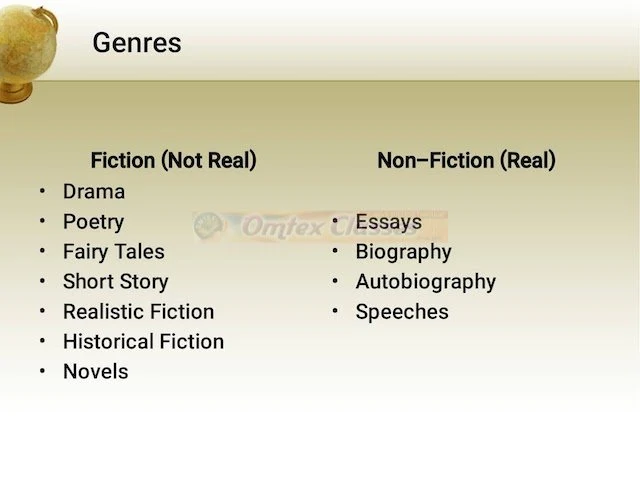
4.1 History of Novel
Novella
The word ‘novella’ originates from the Italian word ‘novelle’. It is a type of prose fiction which is shorter than a full-length novel and longer than short stories. It is a well-structured yet short narrative. It is often satiric or realistic in tone. It usually focuses on one incident or issue with one or two main characters and takes place in a single tradition.
Style of the novel:
The language and the techniques used by the author for the narration of the course of events are known as the ‘style’. An author can use extensive vocabulary and high phrases or he may be laconic and write only to the point or he may mix both according to the requirement for meeting his purpose. He may use linguistic devices to make the narrative effective. All these factors decide the ‘texture’ of the narration and create an impact on the readers. It is called the style of the novel.
Types of Novels:
1) Stream of consciousness novel:
Stream of consciousness is a phrase coined by William James in his treatise ‘Principles of Psychology’ in 1890. It is a method of narration that describes happenings in the flow of thoughts in the minds of the characters. Incidents in the plot are in the sequence of their occurrences. The novelist narrates them as they enter the mind of the character. The stream-of-consciousness novel commonly uses the narrative techniques of interior monologue.
2) Psychological novel:
Psychological novel is the work of fiction that treats the internal life of the protagonist or even the other characters as much as the external factors. It is also called psychological realism. It is a work of prose fiction which places more than the usual amount of emphasis on interior characterization, and on the motives, circumstances, and internal action which springs from, and develops, external action. e.g. ‘Great Expectations’ by Charles Dickens.
3) Epistolary novel:
The word ‘epistolary’ derives from the Latin word ‘epistola,’ which means a letter. The epistolary novel is that in which the writer presents the narrative through a series of letters or other documents. Although letters are the most common basis for epistolary novel, diary entries are also a popular form of this type. e.g. Pamela (By Samuel Richardson), Diary of a Young Girl (By Anne Frank) etc.
4) Autobiographical novel:
The autobiographical novel is the novel based on the life of the author. However, the author changes the places and names of characters or even may change or avoid certain details of his life. It may or may not be in the first-person narration. e.g. David Copperfield by Charles Dickens
5) Gothic novel:
The novels that include terror, mystery, horror, thriller, supernatural, doom, death or decay or haunted buildings are called The Gothic novels. It is a genre associated with the mystery and intrigue surrounding the supernatural and the unknown. Characteristics of the Gothic include: death and decay, haunted homes/castles, family curses, madness, powerful love/romance, ghosts, and vampires. e.g. Dracula by Bram Stoker.
6) Utopian/ Dystopian novel:
Utopia is an imaginary community or society possessing the ideal qualities. It is a common literary theme, especially in science fiction or speculative fiction. Both utopias and dystopias share characteristics of science fiction and fantasy, and both are usually set in a future in which technology has been used to create perfect living conditions. However, the focus of the novel is usually not on the technology itself but rather on the psychology and emotions of the characters who live under such conditions. e.g. ‘Gulliver’s Travels’ by Jonathan Swift.
Indian tradition of novels:
‘Rajmohan’s Wife’, by Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyaya was the first novel in English written by an Indian. The period after that is marked by few more novels written by the Indian writers. These novels bore either nationalistic virtues or social issues as their main framework. Mulkraj Anand, R.K. Narayan and Raja Rao were the major trio who prevailed in the period after that. Novelists like Anita Desai, Nayantara Sahgal, Arun Joshi and Manohar Malgaonkar changed the current of Indian English novel through their works. Amitav Ghosh, Vikram Seth and Upamanyu Chatterjee changed the Indian novel in English by adding new features to it. Recent years have witnessed the dazzling performance by Indian novelists like Salman Rushsie, Arvind Adiga, Arundhati Roy, Kiran Desai and Kiran Nagarkar. The tradition of Indian English novels has undergone a vital change since its birth and it undoubtedly has a very bright future.
---------------------------------------------------------------
Activities:-
1) Rewrite the statements and state whether they are true or false.
a) A Novel is relatively a short narrative.
b) Middle class people had a little interest in romances and tragedies.
Answer: -
a) A Novel is relatively a short narrative. - False
b) Middle class people had a little interest in romances and tragedies. - True
.
Chapter 4: History of Novel
Match the columns:
SOLUTION:
Pick out the odd element from the group.
Arun Joshi, Vikram Seth, Graham Greene, Kiran Nagarkar
SOLUTION:
Graham Greene.
All the others are authors of Indian origin.
Place, Period, Theme, Climate, Lifestyle
SOLUTION:
Theme
All the others are details related to the setting of the novel.
Theme, Plot, Character, Novella
SOLUTION:
Novella
All the others are elements of the novel/novella.
Complete the following statement:
The two types of conflicts that the plot may have are _______.
SOLUTION:
The two types of conflicts that the plot may have are internal (inside the mind of the character) and external (with other characters or entities).
The word ‘picaresque’ originated from _______.
SOLUTION:
The word ‘picaresque’ originated from the Spanish word, ‘picaro’ which means ‘rogue’.
The epistolary novel presents the narrative through _______.
SOLUTION:
The epistolary novel presents the narrative through series of correspondence or other documents.
In the eighteenth century, the middle class could get time for reading and discussing novels because _______.
SOLUTION:
In the eighteenth century, the middle class could get time for reading and discussing novels because of the spread of machines.
Write a short note on:
Style of the novel
SOLUTION:
The language and techniques used by the author to describe the series of events in the story is known as ‘style’. The author can either use a wide range of sophisticated words or he may choose to be concise and to the point. This depends upon which better suits the purpose of the story and is decided by the author. The author may also make use of linguistic devices to make his story more effective and powerful.
Stream of consciousness novel
SOLUTION:
‘Stream of consciousness’ is a phrase coined by William James in his treatise ‘Principles of Psychology.’ (1890). It is an expression of the character’s flow of thoughts in the form of words. The incidents in the plot are in the sequence of their occurrences. The plot is presented through the thought process of the character and thus, the details of the story appear as they enter the mind of the character.
Novella
SOLUTION:
The word ‘Novella’, is derived from the Italian word ‘novelle’ which means ‘new’. The Novella is a type of prose fiction which is shorter than a full length novel and longer than a short story. It is a short, well-structured story, whose tone is usually satirical (of mocking nature) or realistic (depicting reality). It usually focuses on one incident or issue with one or two main characters and takes place in a single tradition.
Indian tradition of novels
SOLUTION:
The Indian tradition of novels in English began with the novel titled, ‘Rajmohan’s Wife’. Written by Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyaya, the novel was first serialized in ‘The Indian Field’. The period that followed saw a few more novels written by Indian writers that focused on nationalistic ideas or social issues. The period after that was ruled by the works of Mulkraj Anand, R.K. Narayan and Raja Rao. Novelists like Anita Desai, Nayantara Sahgal, Arun Joshi, and Manohar Malgonkar shaped the face of the Indian English novel through their works. Amitav Ghosh, Vikram Seth, and Upamanyu Chatterjee further uplifted the Indian English novel by making important additions to its form. Among the recent Indian novelists, noteworthy contributions have been made by Salman Rushdie, Arvind Adiga, Arundhati Roy, Kiran Desai, and Kiran Nagarkar. The Indian English novel has undergone a vital change since its origin and its future appears bright.
.