Chapter 14: Ecosystems and Energy Flow
Multiple choice question
Which one of the following has the largest population in a food chain?
Producers
Primary consumers
Secondary consumers
Decomposers
The second trophic level in a lake is ________________.
Phytoplankton
Zooplankton
Benthos
Fishes
Secondary consumers are __________.
Herbivores
Producers
Carnivores
Autotrophs
What is the % of photosynthetically active radiation in the incident solar radiation?
100%
50 %
1-5%
2-10%
Give the term used to express a community in its final stage of succession?
End community
Final community
Climax community
Dark community
After landslide which of the following type of succession occurs?
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Climax
Which of the following is most often a limiting factor of the primary productivity in any ecosystem.
Carbon
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Sulphur
Very short answer question
Give an example of an ecosystem that shows an inverted pyramid of numbers.
Solution:
A tree ecosystem is an example of an inverted pyramid of numbers.
Give an example of an ecosystem that shows an inverted pyramid of biomass.
Solution:
The oceanic ecosystem is an example of an inverted pyramid of biomass.
Which mineral acts as a limiting factor for productivity in an aquatic ecosystem.
Solution:
Phosphorus.
Name the reservoir and sink of carbon in the carbon cycle.
Solution:
i. Reservoir of carbon in the carbon cycle in the atmosphere and ocean.
ii. Carbon which is present in the rock and fossil fuels like oil, coal and natural gas are the sink of the carbon cycle.
Distinguish between the upright and inverted pyramid of biomass.
Distinguish between Food chain and food web
Long answer question
Define ecological pyramids.
Solution:
An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation of various environmental parameters such as the number of individuals present at each trophic level, the amount of energy, or the biomass present at each trophic level. Ecological pyramids represent producers at the base, while the apex represents the top-level consumers present in the ecosystem.
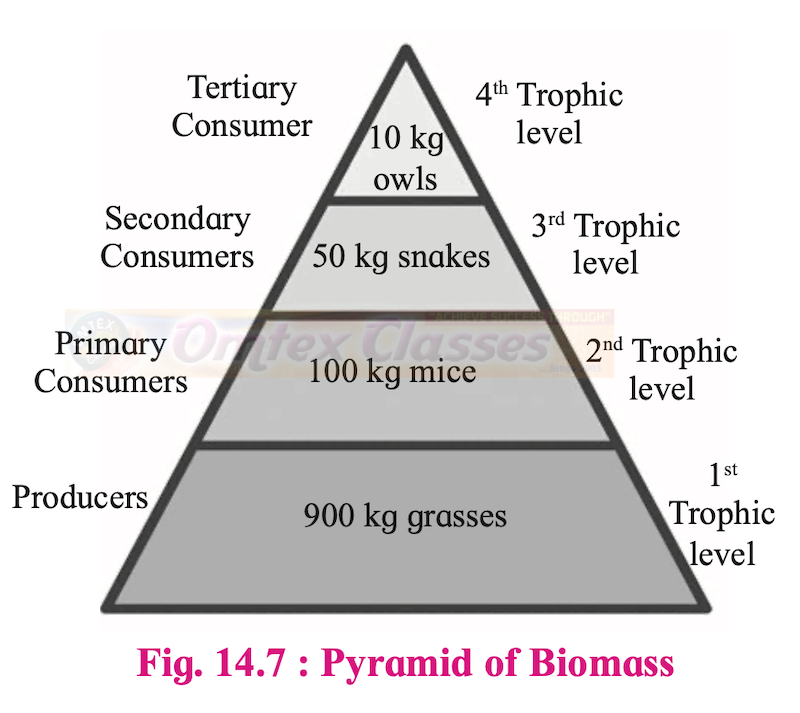
Describe with examples of Pyramids of number, and biomass.
Solution 1:
Pyramid of numbers:
It is a graphical representation of the number of individuals present at each trophic level in a food chain of an ecosystem. The pyramid of numbers can be upright or inverted depending on the number of producers. For example, in a grassland ecosystem, the pyramid of numbers is upright. In this type of a food chain, the number of producers (plants) is followed by the number of herbivores (mice), which in turn is followed by the number of secondary consumers (snakes) and tertiary carnivores (eagles). Hence, the number of individuals at the producer level will be the maximum, while the number of individuals present at top carnivores will be least.
On the other hand, in a parasitic food chain, the pyramid of numbers is inverted. In this type of a food chain, a single tree (producer) provides food to several fruit eating birds, which in turn support several insect species.
Pyramid of biomass
A pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation of the total amount of living matter present at each trophic level of an ecosystem. It can be upright or inverted. It is upright in grasslands and forest ecosystems as the amount of biomass present at the producer level is higher than at the top carnivore level. The pyramid of biomass is inverted in a pond ecosystem as the biomass of fishes far exceeds the biomass of zooplankton (upon which they feed).
What is primary productivity?
Solution:
Primary productivity:
Primary productivity is the rate of generation of biomass in an ecosystem that is expressed in units of mass per unit surface (or volume) per unit time i.e. g/m2/day.
The mass unit may relate to dry matter or to the mass of carbon generated.
Give a brief description of the factors that affect primary productivity.
Solution:
Factors that affect primary productivity are as follows:
a. It depends on the plant species inhabiting a particular area.
b. It depends upon environmental factors such as light, temperature, water, precipitation, etc.
c. It depends upon the availability of nutrients.
d. It also depends upon the photosynthetic capacity of plants. The greater the photosynthetic activity, the higher will be the primary productivity.
Define decomposition.
Solution:
i. Decomposition is the process of breakdown of complex organic matter into inorganic substances like carbon dioxide, water, and nutrients by the decomposers.
ii. Raw materials for decomposition are dead remains of plants and animals, fecal matter, detritus.
iii. This process requires oxygen. Temperature and soil moisture are important factors that indirectly help soil microbes for decomposition.
iv. Warm and the moist environment favours decomposition whereas, low temperature and anaerobic conditions inhibit the process.
Describe the processes and products of decomposition.
Solution:
The steps of decomposition are fragmentation, leaching, catabolism, humification, and mineralization.
a. Fragmentation: Detritivores like earthworm breakdown detritus into smaller fragments or particles.
b. Leaching: In this process, water-soluble inorganic nutrients percolate into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts.
c. Catabolism: The bacterial and fungal enzymes degrade detritus into simpler inorganic substances. All of the above steps occur simultaneously.
d. Humification: It leads to the accumulation of particularly decomposed, a dark coloured, amorphous, colloidal organic substance called humus. Humus serves as a reservoir of nutrients. It is resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate. Humus changes the soil texture and increases the capacity of water holding in the soil.
e. Mineralization: Some microorganisms degrade humus and release inorganic nutrients by the process of mineralization.
Decomposition cycle
Write important features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem.
Solution 1:
Sedimentary cycles have their reservoirs in the Earth’s crust or rocks. Nutrient elements are found in the sediments of the Earth. Elements such as sulphur, phosphorus, potassium, and calcium have sedimentary cycles.
Sedimentary cycles are very slow. They take a long time to complete their circulation and are considered as less perfect cycles. This is because during recycling, nutrient elements may get locked in the reservoir pool, thereby taking a very long time to come out and continue circulation. Thus, it usually goes out of circulation for a long time.
Solution:
Features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem are as follows:
a. Earth’s crust is the main reservoir of phosphorus and other minerals, such as calcium and potassium that undergo sedimentary cycles.
b. The rate of release of minerals that take part in the sedimentary cycle is regulated by various environmental factors temperature, moisture, and nature of the soil.
c. Sedimentary cycles are slower than the gaseous cycles therefore they take more time to complete.
d. Sedimentary cycles are considered as less perfect cycles as, during recycling, nutrient elements may get locked in the reservoir pool, thereby taking a very long time to come out and continue circulation
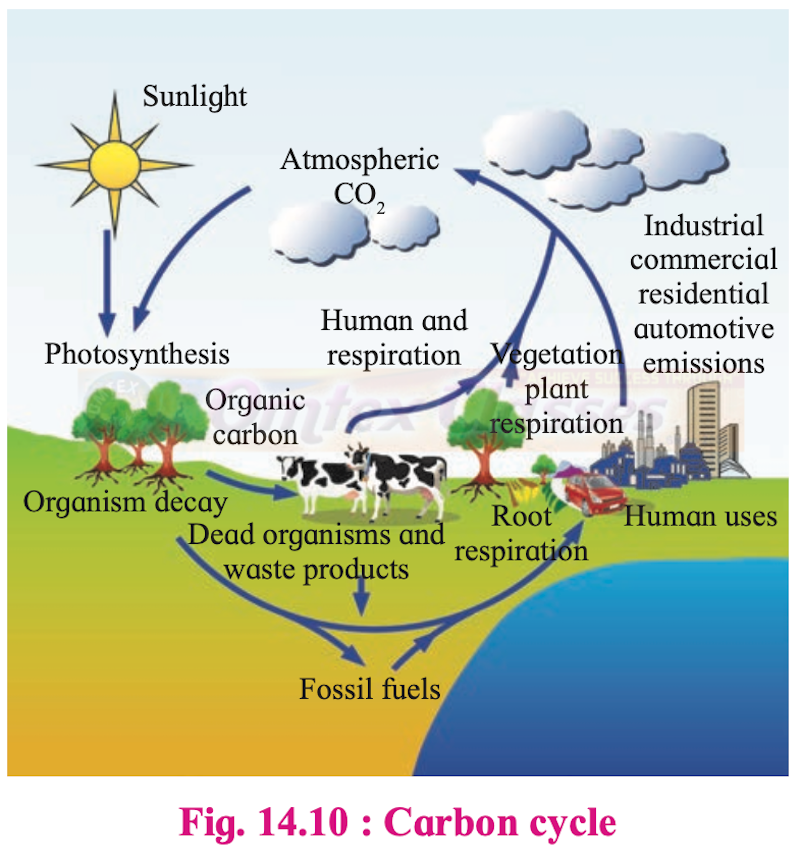
Describe the carbon cycle and add a note on the impact of human activities on the carbon cycle.
Solution:
i. Reservoir of carbon:
a. All life forms on earth are carbon-based because carbon is the main component of all the organic compounds of protoplasm. It constitutes 49% of the dry weight of organisms.
b. 71% of carbon is found dissolved in oceans. The oceanic reservoir regulates the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
c. Carbon present in the rock and fossil fuels like oil, coal, and natural gas has been away from the rest of the carbon cycle for a long time. These long term storage places are known as the sink.
d. The element carbon is a part of seawater, the atmosphere, rocks such as limestone and coal, soils, as well as all living things.
ii. Cyclic pathway of carbon:
a. Carbon as CO2 moves from the atmosphere to plants during the process of photosynthesis to produce food.
b. Carbon moves from plants to animals, through food chains.
c. At the time of exhalation, the CO2 gas is released into the atmosphere. Thus, carbon moves from living things to the atmosphere.
d. Decomposers also contribute substantially to CO2 in the atmosphere, by their processing of waste materials and dead organic matter of land and oceans.
e. When fossil fuels burn to power factories, power plants, motor vehicles, most of the carbon quickly enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide gas.
f. Most of the remainder is dissolved in seawater and deposited as calcium or magnesium carbonate compounds that make up shells of marine animals.
g. The additional sources for releasing CO2 in the atmosphere are the burning of wood, forest fire and combustion of organic matter, fossil fuel, and volcanic activity.
h. The ocean absorbs some carbon in the form of CO2 from the atmosphere. This carbon gets dissolved in the ocean water. Some amount of the carbon which is fixed is lost to sediments and removed from circulation.
iii. The impact of human activities on the carbon cycle
a. Carbon cycle is significantly influenced by human activities.
b. Rapid deforestation and the massive burning of fossil fuel for energy and transport have significantly increased the rate of release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Carbon cycle
Biology 12th Standard
Balbharati Solutions for Biology 12th Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Chapterwise List - Free
Chapter 1: Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants
Chapter 2: Reproduction in Lower and Higher Animals
Chapter 3: Inheritance and Variation
Chapter 4: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Chapter 5: Origin and Evolution of Life
Chapter 6: Plant Water Relation
Chapter 7: Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition
Chapter 8: Respiration and Circulation
Chapter 9: Control and Coordination
Chapter 10: Human Health and Diseases
Chapter 11: Enhancement of Food Production
Chapter 13: Organisms and Populations
Chapter 14: Ecosystems and Energy Flow
Chapter 15: Biodiversity, Conservation and Environmental Issues
Board Paper With Solutions
MARCH 2013, OCTOBER 2013, MARCH 2014, OCTOBER 2014, MARCH 2015, JULY 2015, MARCH 2016, JULY 2016. MARCH 2017, JULY 2017