SSC Geography Model Set 2021-2022 (English Medium) 10th Standard Board Exam Question Paper Solution.
Academic Year: 2021-2022
Date: March 2022
Marks: 40
1) All the activities/questions are compulsory.
2) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
3) Use of stencil is allowed for drawing map
4) Draw neat diagrams and sketches wherever necessary
5) Answers should be written in Black and Blue ink only.
6) Use of pencil/colour pencil is allowed for diagrams, sketches and map work.
7) Answers written in pencils will not be considered.
Multiple Choice Questions
India’s per capita income is less than Brazil due to ____________.
OPTIONS
Low national income
Massive Population
Big family size
Low foodgrain production
To the foothills of the Aravalis ______.
OPTIONS
lies the Bundelkhand Plateau.
lies the Mewad Plateau.
lies the Malwa Plateau.
lies the Deccan Plateau.
Choose the correct option from the following statement:
The highest peak in the Western Ghats is___________________.
OPTIONS
Annaimudi
Dodabetta
Annamalai
K-2
Which of the following shapes show the coastal part of Brazil correctly?
OPTIONS
SOLUTION
Match the columns.
SOLUTIO
Explanation
a. Trans-Amazonian is an important highway in Brazil. It was inaugurated on 27 September 1972. It is 4000 km long. It is the third-largest highway in Brazil. It was commissioned to integrate the interior northern parts of Brazil with the rest of the country.
b. Golden quadrilateral is an important national highway network of India. It connects the major centres of India and the four metros- Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata. It is maintained by the National Highway Authority of India. It was completed in 2012. It is the largest highway project undertaken in India.
c. Rio de Janeiro is an important tourist place in Brazil situated in the 40 ̊ W Meridian. Its proper coordinates are 22 ̊ 54 S, 43 ̊ 12 W. It has the second-largest economy of Brazil.
d. Manmad is a major railway station of the Central Railway zone. It is located in Nasik district of Maharashtra, India. It was opened in 1886.
Attempt Any Four
State whether the sentence is right or wrong and correct the wrong ones and rewrite the sentence
Brazil is mainly located in the Southern hemisphere.
OPTIONS
True
False
SOLUTION
True: Some part of Brazil lies in the northern hemisphere while most of it lies in the southern hemisphere
India faces tropical cyclones frequently.
Tropical cyclones occur often in India.
OPTIONS
Right
Wrong
SOLUTION
Right
Tropic of Capricorn passes through the middle of India.
OPTIONS
Right
Wrong
SOLUTION
Tropic of Capricorn passes through the middle of India - Wrong
Correct Statement - Tropic of Cancer passes from the middle of India.
OR The Tropic of Capricorn passes from the southern part of Brazil.
The river Ganga originates from the Yamunotri glacier.
OPTIONS
True
False
SOLUTION
Flase: The river Ganga originates from the Gangotri glacier and crosses the Himalayas to become an east flowing river.
Like the Indian economy, the Brazilian economy is also of mixed type.
OPTIONS
True
False
SOLUTION
True: Like the Indian economy, the Brazilian economy is also a mixed economy. Both the Indian and the Brazilian economies are developing economies.
Fill the following in the given outline map and also prepare an index.
i) Drought Quadrilateral
ii) Region of orographic rainfall
iii) Savannah region
iv) Caatinga (Thorny bushes)
v) Region with high population density
vi) Region in the south with medium population density
SOLUTION
Fill the following in the given outline map and also prepare an index.
Observe the given map and answer the questions given below it (any four) :
What does the map show ?
Name any two airports from Eastern coast.
In which states, railway routes do not exist ?
Name the Southernmost railway station of India.
Which is the important railway station on the route of Mumbai Mangalore ?
Name the Northernmost airport of India.
SOLUTION
Railway routes & airport
Visakhapatnam & Howrah
Jammu & Kashmir
Kanyakumari
Vasco-da-Gama
Delhi
Attempt Any Two
Give geographical reason.
It is necessary to take items required for field visit and then questionnaires along with us.
SOLUTION
Points - need various items for field visit
- examples - camera for clicking photographs
- questionnaire helps to collect the information on the field visit.
The largest variety of flora is found in Brazil.
SOLUTION
Points - brazil location
- varied climate
- varied vegetation
Like India, there is a need for conservation of forests in Brazil too.
SOLUTION
1) A wide variety of wildlife is found in Brazil because it has high diversity, especially in the Amazon rainforests.
2) Evergreen forests are found in this region around the Amazon basin as it rains throughout the year.
3) Because of the deposition of sediments brought up by the river amazon and as the amazon canal is 150km in width, it forms ideal conditions in terms of soil and water for the growth of dense forests.
4) Apart from the numerous species found in the tropical rainforests of the north, they are also found in the swamps, grasslands, deciduous forests, etc.
5) Forests in Brazil also need conservation like India because they are under the threat of commercial activities like deforestation and pollution.
6) Traditional agricultural practices like slash and burn are also a cause of destruction.
7) In India, the government is taking various initiatives to protect the wildlife of India by bringing in laws against poaching and creating awareness on animal protection like the ‘Project Tiger’, etc.
Vegetation is scarce in the high altitudes of Himalayas.
SOLUTION
1) The climate is very cold in the high altitudes of the Himalayas.
2) During winters, in Jammu & Kashmir and parts of mountainous regions of Himalayas, the temperatures drop to - 40° C. There is heavy snowfall.
3) Due to this, land which is covered with snow becomes unsuitable for vegetation. Hence, seasonally flowering trees are found here. Therefore, due to very cold temperatures, vegetation is scarce in the high altitudes of Himalayas.
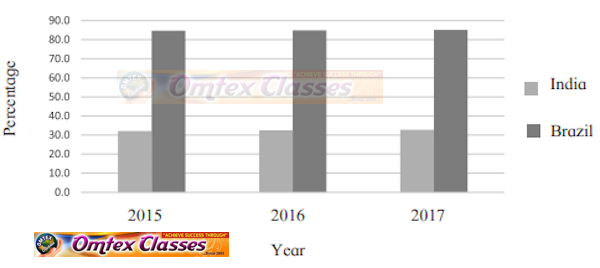
Prepare a multiple bar graph on the basis of the given information and answer the questions.
India and Brazil – Urban population (%)
1) What is the percentage of urban population in India in 2017?
2) In which country is the percentage of urban population higher?
3) What does the trend in urban population in both the countries indicate?
SOLUTION
India and Brazil - Urban population (%)
Scale - 1 cm = 10%
1) - 32.8 %
2) - Brazil
3) - Rate of urbanisation is low in Brazil and high in India.
Study the graphs given in figure and answer the following questions:
1) What difference do you find in the rainy seasons of Chennai and other cities of India? Why?
2) What similarity do you see in the temperature curves of Delhi and Kolkata?
3) Calculate the average range of minimum and maximum temperatures of all the four cities.
4) In which city is the range minimum? What can you infer from this?
5) In which city is the range maximum? What can you infer from this about its climate?
6) Based on the temperature and rainfall of Mumbai, comment upon its climate.
7) In which month does India experience the highest rainfall?
8) Classify the cities as cities with equable and extreme climates.
SOLUTION
(i) Chennai ranks second in terms of the amount of rainfall. It receives winter rainfall which is not seen in other cities.
(ii) From the temperature curves, Delhi and Kolkata seem to have extreme temperatures.
(iii) Delhi min: 31.3 Max: 16.08
Kolkata min: 32.1 Max: 21.08
Mumbai min: 31.83 Max: 22.16
Chennai min: 33.1 Max: 24.41
(iv) The range is minimum in Delhi. The climate of Delhi is an overlap between monsoon-influenced Humid subtropical and semi-arid with high variation between summer and winter temperatures and precipitation.
(v) The range is maximum in Chennai. Chennai has a Tropical wet and dry climate. The city lies on the thermal equator and is also on the coast, which prevents extreme variation in seasonal temperature.
(vi) The Climate of Mumbai is a Tropical wet and dry climate. Mumbai's climate can be best described as moderately hot with a high level of humidity.
(vii) India experiences the highest rainfall in the month of July.
(viii) Extreme: Delhi, Kolkata
Equable: Mumbai, Chennai
Answer in detail (Attempt Any Two)
Describe the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India and Brazil.
SOLUTION 1
1) Longitudinal and latitudinal extent of Brazil:
Brazil being the 4th largest country in the world.
The Longitudinal extent of Brazil is an area 4,319 kilometers from east to west 34°47'30" E to 73°59'32" W (34 degrees 47 minutes 30 seconds E to 73 degrees 59 minutes 32 seconds W longitude) and
The Latitudinal extent of Brazil extends 4,395 kilometers from north to south 5°16'N to 33°44'S (5 degrees 16 minutes 20 seconds N to 33 degrees 44 minutes 32 seconds S latitude).
2) Longitudinal and latitudinal extent of India:
India being one of the biggest countries in Asia.
The Longitudinal extent of India has an area of 2933 kilometers from east to west. 68°7' E to 97°25' E (68 degrees 7 minutes E to 97 degrees 25 minutes E longitude) and
The Latitudinal extent of India extends 3214 kilometers from North to South 37°6' N to 8°4' N (37 degrees 6 minutes N to 8 degrees 4 minutes N latitude)
The difference in the longitudinal and latitudinal extent of India and Brazil is ≅ 10 degrees with Brazil being longer.
SOLUTION 2
The latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India and Brazil is as follows:
Indira Point is the southernmost tip of India and it is located on 6°45'N parallel.
1) Compare and classify the population densities shown in the squares ‘a’ and ‘b’ representing 1 sq.km of area.
2) If in figure b, one sign = 100, then what will be the sex ratio?
(a)
(b)
SOLUTION
The density of population in figure (a) is less than the density of population in figure (b). Thus, figure (a) shows sparse population while figure (b) shows dense population.
Given that, one sign = 100 persons.
Since, there are 10 female signs, there are:
10 × 100 = 1000 females
Since, there are 8 male signs, there are:
8 × 100 = 800 males
If number of males = 1000,
then number of females =?
∴ Sex ratio =
1000×1000800
= 1250
∴ The sex ration in this case is favourable.
What could be the reasons of lower sex ratio in any region?
SOLUTION
Sex ratio refers to the number of females per thousand males in a region. India has a low sex ratio.
The reasons for lower sex ratio are as follows:
a. Illiteracy:
People are not aware of the role of women in modern society. This is because of child marriages where girls get married at an early age without having a chance to study and educate themselves.
b. Female infanticide:
Even though the Government has passed many Acts to stop this inhuman act, people still prefer to have a male child due to many reasons. Hence, girl babies are killed as soon as they are born.
c. Domestic violence:
Women are considered to be the weaker sex and hence crimes and violence against women is still a common feature in many of the rural households. This makes even the mother stop having a girl child.
d. Female foeticide:
Due to socio-economic issues like dowry, people destroy the girl foetus in the womb itself. Many laws have been made to prevent this.
e. Poverty:
Poverty is a major reason for the declining sex ratio. Families living under Below Poverty Line(BPL) generally do not want to have girl children.
f. Lack of women empowerment:
Due to lack of education, women do not enjoy equal opportunities in many of the rural areas, especially in northern India.
The lower sex ratio, even in the twenty-first century is really a cause of concern.
What are the similarities and differences in the fishing activities in Brazil and India?
SOLUTION
i) Brazil has a sea coast of around 7,400 km and excellent fishing grounds off the South Atlantic coast.
ii) The meeting of the warm Brazil current and the cold Falkland current off the coast of south-east Brazil makes it a good fishing ground.
iii) Traditionally, fishing has been carried on by small groups of individual fishermen using primitive techniques and equipment.
iv) But now, large vessels are being used. Swordfish, shrimp, lobsters, sardines are mainly caught. v) The fish resources of the Amazon River are not exploited much and fishing only take place at a small scale.
vi) Fishing in India : Fishing play an important role in the economy of India. India is one of the largest producers of fish, both marine and inland. Fisheries help in augmenting food supply, generating employment, raising nutritional level and earning foreign exchange.
viii) India has about 7500 kms of coastline. Marine fishing accounting for about 40 per cent of the total annual production of fish and being confined to coastal waters in the west from Kachchh, Malabar coast to Coromandel coast in the east. Major fishes are sardines, mackerel, Bombay duck,and prawns. On the eastern coast, the important fish are horse mackerels, clupeids and silver bellies.
ix) Freshwater fishing is carried on in rivers, canals, irrigation channels, tanks, ponds, lakes, etc. Silver bellies carp (chopda) etc. are major freshwater varieties. About 60 per cent of the country’s total fish production comes from inland fisheries.
Balbharati Solutions for Social Science Geography 10th Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board
Geography 2020-2021 SSC (English Medium) 10th Standard Board Exam Question Paper Solution.
Balbharati Solutions for Social Science Geography 10th Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board
Chapter 2: Location and Extent
Chapter 3: Physiography and Drainage
Chapter 5: Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Chapter 8: Economy and Occupations