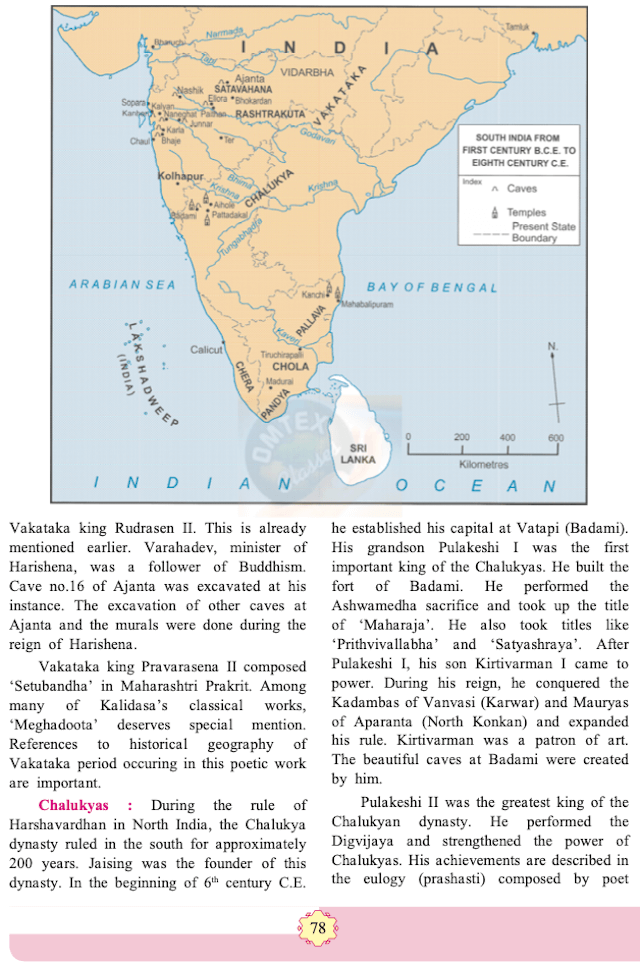
Chapter 11: Kingdoms in South India
Choose the correct alternative and write the complete sentence.
The name of the well-known king of Vakatak dynasty was ______.
OPTIONS
Sarvasena
Pravarasena
Jaising
Chandragupta
SOLUTION
The name of the well-known king of Vakatak dynasty was Pravarasena.
After the conquest in South, Pulakeshin II took up the title of ______.
OPTIONS
Parameshwara
Vishayapati
Deshadhipati
Satyajay
SOLUTION
After the conquest in South, Pulakeshin II took up the title of Parameshwara.
Kalidasa composed ______ at Ramtek in Vidarbha.
OPTIONS
Shakuntal
Meghdoot
Malavikagnimitra
Harivijay
SOLUTION
Kalidasa composed Meghdoot at Ramtek in Vidarbha.
The world famous Kailasa temple was built during the ______ period.
OPTIONS
Chalukya
Pallava
Cher
Rashtrakuta
SOLUTION
The world famous Kailasa temple was built during the Rashtrakuta period.
Find the incorrect pair from set B and write the correct ones.
SOLUTION
Explain the following statement with reasons.
A strong rule of the Chalukyas was created in south India
SOLUTION
The Chalukya dynasty ruled in the south for approximately 200 years.
Jaising the founder of this dynasty established his capital at Vatapi (Badami) Pulakeshin I was an important king of this dynasty who performed the Ashwamedha sacrifice.
After him, his son Kirtivarman I came to power. During his reign, he conquered the Kadambas of Vanvasi (Karwar) and Mauryas of Aparanta (North Konkan) and expanded his rule.
The greatest king of the Chalukyas was Pulakeshin II.
He performed the Digvijaya and strengthened the power of the Chalukyas.
His achievements are described by Ravikirti, a poet. He defeated Harshavardhan thus, acquiring great fame.
Yadava period has a special importance in the history of Maharashtra.
SOLUTION
Yadava dynasty is one of the important dynasties of Medieval Maharashtra.
During this period there was a notable development in the cultural sphere of Maharashtra.
The Mahanubhav and Warkari sects had a beginning in the Yadava period.
During this period, Patan in Khandesh, Solotagi in Karnataka, and Paithan in Maharashtra became important centres of learning.
Sanskrit texts were written on subjects like Dharmashastra, 'Purva Mimansa' (philosophical text), Nyaya and Vedanta.
Many important texts were composed at this time for eg. composition of saint poets like Namadeva, Janabai etc. Many temples were built of the Hemadipanti style at this time.
An important feature of the Hemadipanti temples is that no mortar was used.
Write short notes.
Administrative system in South India
SOLUTION
There were officials like 'Mahadandanayaka', 'Rashtrika', 'Deshadhikruta', 'Amatya', 'Ayukta', etc.
The council of officers in the Chola kingdom was called 'Udankuttam'.
The kingdom was divided into many provinces. These provinces were known as 'Mandalam'.
A member of the royal family was the chief of the Mandalam.
There were many officers under him such as 'Vishayapati', 'Deshadhipati', 'Deshadhikrut', 'Rashtrika', etc.
The administration of the Southern kingdoms was very efficient. Village autonomy was an important feature.
The 'Gramasabha' (village council) looked after the village administration.
The head of the Gramasabha was known by different names such as 'Gramabhojaka', 'Gramakuta' etc.
Land revenue was the main source of income for the state.
Apart from it the excise tax, professional tax, pilgrimage tax were the sources of income.
Coins in South Indian dynasties
SOLUTION
The Maurya coins were in circulation in South India.
After the decline of Mauryas, the Pandyas issued their own punch marked coins.
The images like sun, horse, stupa, tree, fish were carved on it.
On the Chera coins, there used to be a bow and arrow on one side and an image of an elephant on the other.
On the Chola coins, the symbol of the tiger as the royal emblem of Cholas is depicted.
The Chola coins were made of gold, silver and the legends were inscribed in Devnagari script.
The coins belonging to Chalukya king Rajaraja are issued in three metals gold, silver, and copper, with the image of Rajaraja and a tiger.
Due to the trade with Rome, many Roman coins are found.
Answer the following question in brief with the help of points given below.
Describe the rule of Shilahara dynasty.
Founder
Shilahara of south Kokan
Shilaharas of north Kokan
Shilaharas of Kolhapur
SOLUTION
Founder: Jimutvahan is considered to be the founder of all three branches. They ruled for almost three hundred years as the feudatories of Rashtrakutas and later the Chalukyas.
Shilahara of South Konkan: Sanafulla established the South Konkan branch of Shilaharas. His son, Dhammiyar set up the village ofVallipattana and built a fort there. Later King Adityavarma expanded his kingdom from Thane to Goa. Rattaraj was the last ruler of this dynasty. One of the copper plates found at Kharepatan gives an account of the history of this dynasty.
Shilaharas of North Konkan: Kapardi established the North Konkan branch of Shilaharas. Their capital was at Sthanak (Thane). Aparajita was an important king of this branch. He ruled for around thirty-five years. He was followed by Chittaraj.
Shilaharas of Kolhapur: The modern districts of Satara, Sangli, Ratnagiri, and Belgaum were included in this kingdom. Jatiga established the Kolhapur branch of Shilaharas. Bhoj II was an important king of this dynasty. Kolhapur, Valivade, and Panhala were the capitals of this kingdom. 'Koppeshwar Mahadev' temple at Khidrapur was the creation of Shilaharas.
Balbharati Solutions for History 11th Standard Maharashtra State Board
• Chapter 2: First Cities of India
• Chapter 3: Chalcolithic Villages in India
• Chapter 5: Janapadas and Republics
• Chapter 6: Second Urbanisation in India
• Chapter 7: India and Iran (Persia)
• Chapter 8: India during Mauryan period
• Chapter 9: Post Mauryan India
• Chapter 11: Kingdoms in South India
• Chapter 12: India, Nations in the northwest of the Indian Subcontinent and China
• Chapter 13: India, Shri Lanka and Southeast Asia
• Chapter 14: Delhi Sultanate, Vijayanagar and Bahamani Kingdom
• Chapter 15: India during Mughal period
• Chapter 16: Swarajya to Empire (Maratha period)
.
Balbharati Solutions for History 11th Standard Maharashtra State Board
• Chapter 2: First Cities of India
• Chapter 3: Chalcolithic Villages in India
• Chapter 5: Janapadas and Republics
• Chapter 6: Second Urbanisation in India
• Chapter 7: India and Iran (Persia)
• Chapter 8: India during Mauryan period
• Chapter 9: Post Mauryan India
• Chapter 11: Kingdoms in South India
• Chapter 12: India, Nations in the northwest of the Indian Subcontinent and China
• Chapter 13: India, Shri Lanka and Southeast Asia
• Chapter 14: Delhi Sultanate, Vijayanagar and Bahamani Kingdom
• Chapter 15: India during Mughal period
• Chapter 16: Swarajya to Empire (Maratha period)
.