Chapter 8: India during Mauryan period
Choose the correct alternative and complete the sentence.
The first well-known king of the Haryank dynasty is ______.
OPTIONS
Chandragupta Maurya
Bimbisara
Ajatashatru
Mahapadma
The Nanda dynasty was established by ______.
OPTIONS
Dhanananda
Shishunaga
Mahapadma Nanda
Emperor Ashoka
The great drama in Sankrit literature, Swapnavasavadatta, was written by ______.
OPTIONS
Kautilya
Bharat
Kalidasa
Bhasa
Find out the incorrect pair, correct it and rewrite.
OPTIONS
Built the foundation of Magadha Empire – Bimbisara
Brought an end to Nanda rule – Chandragupta Maurya
Chinese traveler who visited India during the period of Chandragupta Maurya – Megasthenes
Changed his mind due to the destruction in Kalinga war – Emperor Ashoka
SOLUTION
Greek ambassador who visited India during the period of Chandragupta Maurya – Megasthenes
Choose the correct reason and complete the sentence.
Emperor Ashoka erected many pillars.
Reason ______.
OPTIONS
Spread of Art
Spread of ‘Dhamma’
Growth of trade
For recognition of his work
Explain the following statement with reasons.
Ashoka’s victory at Kalinga proved to be a turning point in history as well as the life of Ashoka.
SOLUTION
There was a great loss of human life in this (Kalinga)war. Ashoka became victorious.
The destruction caused due to the Kalinga war brought about a great change in the mind of Ashoka.
His mind got diverted towards the non-violent, peaceful Buddhist religion.
The desire of Digvijaya was replaced by Dharma Vijaya (Dhamma Vijaya).
His career proved to be an important because of the religious ideals propagated by him and the creation of a mechanism to until it in people's life.
The war between Chandragupta and the Greek king Seleucus was very important.
SOLUTION
Chandragupta Maurya defeated the Nandas and established the Mauryan dynasty.
In the text of Mahavamsa, Chandragupta is referred as 'the emperor of Jambudvipa i e. emperor of Bharatvarsh'.
The Mauryas created a huge empire by conquering the big and small states in northwest, north and southern regions.
As a consequence, the boundaries of Mauryan Empire extended to the Hindukush in the northwest.
The Mauryan Empire extended from Hindukush to the Bay of Bengal in the east and Gujarat in the west, as well as Himalayas in the north to the Krishna river in the south.
Thus, the war between Chandragupta and the Greek King Seleucus was very important.
The Mauryan administration acquired a definite form.
SOLUTION
Chandragupta Maurya was a valiant king and an efficient administrator.
He setup a defined mechanism of state administration which suited the economic conditions and the needs of the Maurya empire.
The Mauryan emperors created a unified empire.
At the same time, they devised a decentralised administrative system for efficient functionality of the empire.
State your opinion.
Chandragupta Maurya is the first Chakravarti emperor in the history of India.
SOLUTION
The concept of 'Chakravarti' occurs in the literature on ancient Indian polity.
The sovereign ruler whose chariot could roll in all four directions without any obstruction was known as Chakravarti.
It was expected that his rule should be ethical and for the welfare of the state.
During his tenure the wheel of 'Ruta' remains intact. His rule is on an extended territory.
Thus, Chandragupta Maurya was the first Chakravarti Emperor.
The rock edicts of Ashoka are important sources of history.
SOLUTION
The rock edicts and pillar inscriptions are found at many places in the regions of Afghanistan, Nepal and India.
There rock edicts and pillar inscriptions give information about the boundaries of the Mauryan empire.
Ashoka's effects to spreads Buddhist ideals and the written evidence of the spread of Buddhism and Indian culture in distant countries through the Buddhist monks sent by Ashoka occurs in these inscriptions.
Thus, rock edicts of Ashoka are important source of history.
Various trade guilds developed during the Mauryan period.
SOLUTION
During the Mauryan period there was an increase in revenue due to a well-organised taxation system.
Several industries and professions flourished during this period.
As a result of this these professions were organised into trade guilds, for e.g., there were guilds of carpenters, weavers, farmers etc.
Thus, Various trade guilds developed during the Mauryan period.
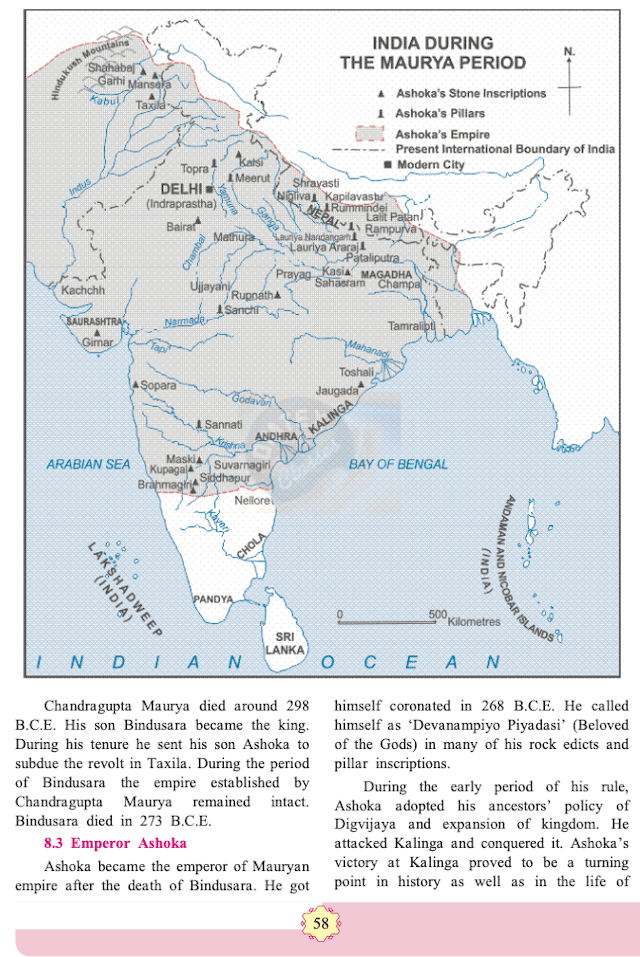
Observe the map and answer the questions based on it.
(1) Regions included in Ashoka’s Empire
(2) Locations of Ashoka’s rock and pillars edicts.
SOLUTION
Regions of Afghanistan, Nepal and India are included in Ashoka's Empire.
Ashoka's rock edicts are found in location such as : Mansera, Taxila, Kalsi, Toshali, Maski, Kupaga, Brahmagiri, Siddhapur, Sapara, Girnar, Kasi, Rupnath, Bairat.
Ashoka's pillar edicts are found in location such as : Topra, Meerut, Nigliva, Rummindei, Lauruja Nandangarh, Saurya, Araraj, Ramparva, Sanchi, Sannati.
Balbharati Solutions for History 11th Standard Maharashtra State Board
• Chapter 2: First Cities of India
• Chapter 3: Chalcolithic Villages in India
• Chapter 5: Janapadas and Republics
• Chapter 6: Second Urbanisation in India
• Chapter 7: India and Iran (Persia)
• Chapter 8: India during Mauryan period
• Chapter 9: Post Mauryan India
• Chapter 11: Kingdoms in South India
• Chapter 12: India, Nations in the northwest of the Indian Subcontinent and China
• Chapter 13: India, Shri Lanka and Southeast Asia
• Chapter 14: Delhi Sultanate, Vijayanagar and Bahamani Kingdom
• Chapter 15: India during Mughal period
• Chapter 16: Swarajya to Empire (Maratha period)
.
Balbharati Solutions for History 11th Standard Maharashtra State Board
• Chapter 2: First Cities of India
• Chapter 3: Chalcolithic Villages in India
• Chapter 5: Janapadas and Republics
• Chapter 6: Second Urbanisation in India
• Chapter 7: India and Iran (Persia)
• Chapter 8: India during Mauryan period
• Chapter 9: Post Mauryan India
• Chapter 11: Kingdoms in South India
• Chapter 12: India, Nations in the northwest of the Indian Subcontinent and China
• Chapter 13: India, Shri Lanka and Southeast Asia
• Chapter 14: Delhi Sultanate, Vijayanagar and Bahamani Kingdom
• Chapter 15: India during Mughal period
• Chapter 16: Swarajya to Empire (Maratha period)
.