ACCOUNTS BOARD QUESTION PAPER : MARCH 2022

SOLUTION TO BK & ACCOUNTANCY MARCH 2022 BK SOLUTION. IMPORTANT FOR BOARD EXAM 2023.
Max. Marks: 80
Time: 3 Hrs.
Q.1. Attempt all of the following sub-questions: [20]
(A) Select the correct options and rewrite the statements:
(1) To find out the net profit or net loss of the business _______ Account is prepared.
(a) Trading
(b) Capital
(c) Current
(d) Profit and Loss
(2) From financial statement analysis the creditors are specially interested to know _______.
(a) Liquidity
(b) Profits
(c) Sale
(d) Share Capital
(3) Death is a compulsory _______.
(a) dissolution
(b) admission
(c) retirement
(d) winding up
(4) The due date of the bill drawn for 2 months on 23rd November, 2019 will be _______.
(a) 23rd Jan, 2020
(b) 25th Jan, 2019
(c) 26th Jan, 2019
(d) 25th Jan, 2020
(5) Decrease in the value of assets should be _______ to Profit and Loss Adjustment Account.
(a) debited
(b) credited
(c) added
(d) none of the above
(B) Write a word / term / phrase as a substitute for each of the following statements: (5)
(1) Debit balance of Trading Account.
Answer: Gross Loss.
(2) Expenses incurred on dissolution of the firm.
Answer. Dissolution/realization Expenses
(3) Old Ratio less New Ratio.
Answer: Sacrifice Ratio
(4) Officer appointed by Govt. for noting the dishonor of the bill.
Answer: Notary Public.
(5) Donation received for a specific purpose.
Answer: Specific donation / Capital receipt.
(C) Answer the following questions in only ‘one’ sentence each: (5)
(1) What is Legacy?
Solution: Any asset, property or amount of cash which ‘Not for Profit’ concern receives as per the provisions made in the will of the donor after his death is called Legacy.
(2) What is CAS?
Solution: CAS means Computerized Accountig System which helps business firms to implement accounting process and makes it user friendly with automation.
(3) Who is called Insolvent Person?
Solution: Whose capital A/c shows debit balance and who is not in a position to meet his capital deficiency even from his private property is called an insolvent person.
(4) What is Reserve Capital?
Solution: Reserve Capital is that part of the subscribed capital which is reserved to be called-up only at the time of winding up or liquidation of the company.
(5) What is Revaluation Account?
Solution: The account which shows change in the values of assets and liabilities during the admission, retirement or death of a partner is known as Revaluation Account.
(D) Complete the sentences: (5)
(1) Partnership deed is an _______ of partnership.
Solution: Partnership Deed is an Article of Partnership.
(2) Aurangabad University prepares _______ Account instead of Profit and Loss Account.
Solution: Aurangabad University prepares Income and Expenditure Account instead of Profit and Loss Account.
(3) Returns outward are deducted from _______.
Solution: Returns outward are deducted from Purchases.
(4) New Ratio (–) _______ = Gain Ratio.
Solution: New Ratio (less) Old ratio = Gain ratio
(5) Cash receipts which are recurring in nature are called as _______ receipts.
Solution: Cash receipts which are recurring in nature are called as revenue Receipts.
Q.2. Ram and Shyam were in partnership sharing profits and losses in the proportion of 3:1 respectively. Their Balance sheet as on 31st March, 2020 stood as follows: [10]
Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2020
They admit Bharat into partnership on 1st April, 2020. The term being that:
(1) He shall have to bring in ₹ 40,000 as his Capital for 1/5th share in future profit and ₹ 20,000 as his share of Goodwill.
(2) A provision for 5% doubtful debts to be created on sundry debtors.
(3) Stock should be appreciated by 5% and Land and Building be appreciated by 20%.
(4) Furniture to be depreciated by 20%.
(5) Capital Accounts of all partners be adjusted in their new profit sharing ratio through Cash Account.
Prepare:
(i) Profit and Loss Adjustment Account
(ii) Partners’ Capital Account.
(iii) Balance Sheet of the new firm.
OR
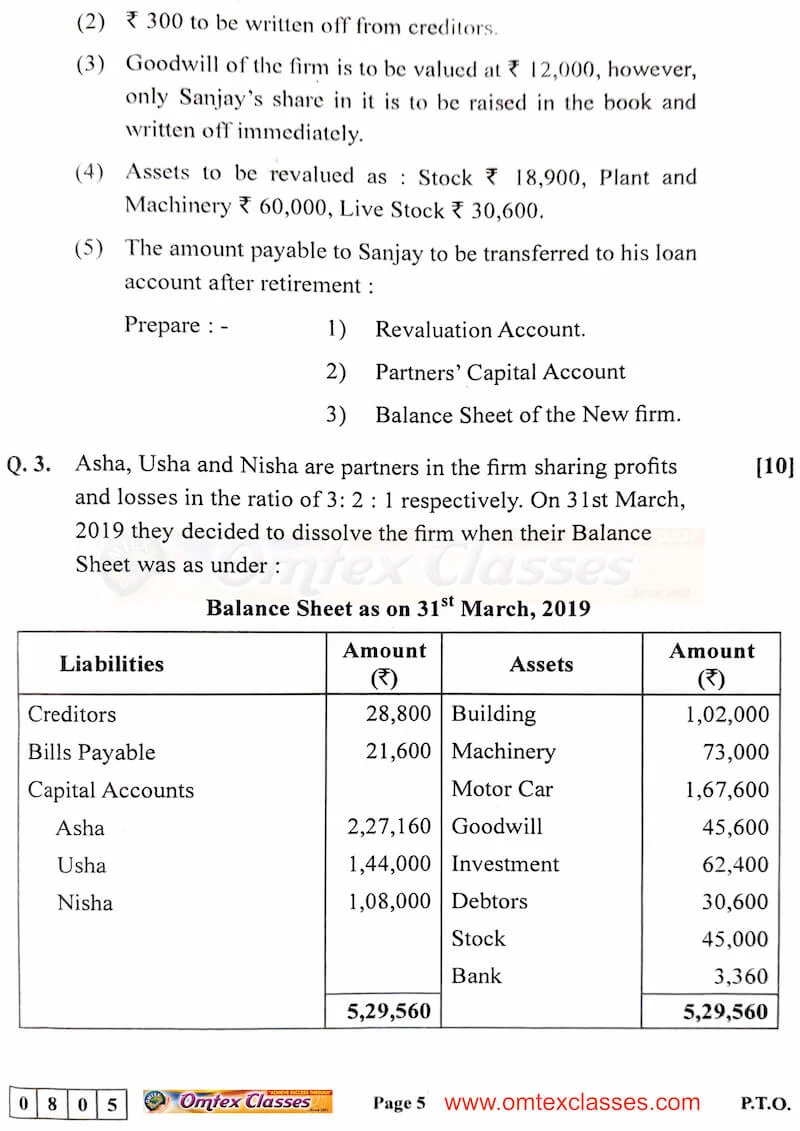
Ajay, Vijay and Sanjay were partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 3 : 2. Their Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2020 is as follows:
Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2020
On 1st April, 2020 Sanjay retired from the firm on the following terms:
(1) R.D.D. is to be maintained at 10% on debtors.
(2) ₹ 300 to be written off from creditors.
(3) Goodwill of the firm is to be valued at ₹ 12,000, however, only Sanjay’s share in it is to be raised in the book and written off immediately.
(4) Assets to be revalued as: Stock ₹ 18,900, Plant and Machinery ₹ 60,000, Live Stock ₹ 30,600.
(5) The amount payable to Sanjay to be transferred to his loan account after retirement:
Prepare:
(i) Revaluation Account.
(ii) Partners’ Capital Account
(iii) Balance Sheet of the New firm.
SOLUTION:
Q.3. Asha, Usha and Nisha are partners in the firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2 : 1 respectively. On 31st March, 2019 they decided to dissolve the firm when their Balance Sheet was as under: [10]
Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2019
The firm was dissolved on the above date and the assets realised as under:
(1) Asha agreed to take over the Building at ₹ 1,23,600.
(2) Usha took over Goodwill, Stock and Debtors at book value and agreed to pay Creditors and Bills payable.
(3) Motor car and Machinery realised at ₹ 1,51,080 and ₹ 31,680 respectively.
(4) Investment were taken by Nisha at an agreed value of ₹ 55,440.
(5) Realisation Expenses amounted to ₹ 6,800.
Prepare:
(a) Realisation Account
(b) Partners’ Capital Account
(c) Bank Account
OR
Sonali draws a bill on Rupali for ₹ 50,000 for 3 months. Rupali accepts the bill on the same date. Sonali sends the bill to the bank for collection. Before due date, Rupali finds herself unable to make payment of bill and requests Sonali to renew it. Sonali agrees to the proposal on a condition that Rupali should pay ₹ 20,000 in cash along with interest ₹ 1,000 and accept a new bill for 2 months for the balance. Rupali retired the bill by paying ₹ 27,000.
Give Journal entries in the books of Sonali and prepare Rupali’s Account in the books of Sonali.
SOLUTION:
Q.4. Ajita Ltd. issued 2,00,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 each at a premium of ₹ 2 per share payable as: [8]
₹ 3 on application
₹ 5 on allotment (including ₹ 2 premium)
₹ 4 on first and final call
Applications were received for 2,40,000 equity shares and pro-rata allotment was made to all the applicants.
The excess application money was adjusted with allotment. Prerna who was allotted 400 shares failed to pay first and final call and her shares were forfeited.
Pass Journal Entries in the books of Ajita Ltd.
SOLUTION:
OR
State the difference between Manual Accounting Process and Computerised Accounting Process.
Solution
Q.5. Anil, Sunil and Mohit were partners sharing profits and losses in the proportion of their capital. Their Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2019 was as follows: [8]
Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2019
Mohit died on 1st August, 2019 and the following adjustments were made:
(1) Assets to be revalued as under:
Land and Building ₹88,000
Motor Lorry ₹ 36,000
Furniture ₹ 34,000
(2) All debtors were good.
(3) Goodwill of the firm valued at two times the average profit of last 4 years’ profit.
(4) Mohit’s share of profit to be calculated on the basis of average profit of the last three years.
(5) Profit for four years 1st year ₹ 12,000, 2nd year ₹ 24,000, 3rd year ₹ 14,000, 4th year ₹ 22,000.
Prepare:
(a) Mohit’s capital account showing the amount payable to his executor.
(b) Give working note of Mohit’s share of goodwill and profit up to the date of his death
SOLUTION:
OR
Following is the Balance Sheet of Param Company Ltd. as on 31st March, 2019 and 31st March, 2020:
You are required to prepare Comparative Balance Sheet of Param Company Ltd. as on 31st March, 2019 and 31st March 2020.
Q.6. From the following Receipts and Payments Account of Shahu College, Kolhapur for the year ending 31st March, 2020 and additional information, prepare Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31st March, 2020 and Balance Sheet as on that date: [12]
Receipts and Payments Account for the year ended 31st March, 2020
Additional information:
(1) Outstanding Salaries ₹ 35,000.
(2) 60% of donations are for Building Fund and Balance is to be treated as revenue income.

SOLUTION:
Q.7. Asha and Nisha are partners sharing profits and losses in equal ratio. From the following Trial Balance and adjustments you are required to prepare Final Accounts: [12]
Trial Balance as on 31st March, 2019
Adjustments:
(1) Closing stock is valued at cost price ₹ 88,000 and market price ₹ 90,000.
(2) Asha and Nisha withdrew goods from business ₹ 3,000 and ₹ 2,000 respectively for their personal use.
(3) Depreciate Motor Van by 5% and Plant and Machinery by 7%.
(4) Reserve for Doubtful debts on Debtors at 5% is to be created.
(5) Outstanding Wages ₹ 800.