Rhyming and Early Childhood Development
Three sources explore the importance of rhyming words in early childhood development. They emphasize the connection between rhyming and phonological awareness, vocabulary expansion, and memory improvement. Practical strategies for teaching rhyming, including games, songs, and visual aids, are suggested. The sources also address challenges children might face and advocate for a multi-sensory approach to learning. Overall, the text promotes the use of rhyming to foster a love of language and reading.
Rhyming Words: A Comprehensive Guide
Rhyming Words: A Briefing Document
This briefing document reviews the main themes and key concepts related to rhyming words, drawing upon three sources: "Rhyming Words: A Comprehensive Study Guide," "Rhyming Words: A Guide for Parents and Educators," and "Testing Theme: Rhyming Words.pdf".
Core Concept: Defining and Understanding Rhyming Words
Rhyming words are words that share the same ending sound. As stated in "Rhyming Words: A Guide for Parents and Educators," "'cat' and 'hat' rhyme because they both end with the 'at' sound." This simple concept has significant implications for early childhood language development.
Importance of Rhyming Words in Language Development
●
Phonological Awareness: A cornerstone of reading and spelling, phonological awareness is the ability to recognize and manipulate sounds within words. Rhyming activities strengthen this skill by attuning children to sound patterns. The "Rhyming Words: A Comprehensive Study Guide" emphasizes that "rhyming words are important for language development because they build phonological awareness."
●
Vocabulary Expansion: Exposure to rhyming words naturally introduces children to new vocabulary with shared sound elements. "Rhyming Words: A Guide for Parents and Educators" highlights this, stating that "Exposure to rhyming words can help children expand their vocabulary by introducing them to new words that share similar sounds."
●
Memory Enhancement: Rhymes create memorable patterns that facilitate information retention. The repetitive sound structure aids recall, particularly for young learners. The guide emphasizes that "Rhyme and memory are interconnected because rhymes create patterns that make information easier to remember."
●
Enjoyment of Language: Rhymes inject an element of fun and playfulness into language learning. This fosters a love of language, poetry, and reading. "Rhyming Words: A Guide for Parents and Educators" notes that "Rhymes make language fun and engaging, fostering a love of reading and poetry."
Practical Strategies and Activities for Teaching Rhyming Words
The sources advocate for a multi-sensory approach, incorporating visual, auditory, and kinesthetic activities to engage children in the learning process. Here are some key strategies:
●
Reading Rhyming Books: Nursery rhymes, Dr. Seuss books, and other rhyming literature expose children to rhyming patterns in a fun and engaging way.
●
Rhyming Games: "I Spy" with rhyming words, creating silly rhymes, and other games make learning interactive and enjoyable.
●
Singing Rhyming Songs: Songs with rhymes naturally develop phonological awareness through rhythm and melody.
●
Using Rhyming Flashcards: Flashcards with pictures and words provide a visual connection to rhyming pairs. "Testing Theme: Rhyming Words.pdf" visually demonstrates various rhyming flashcards with colorful illustrations.
●
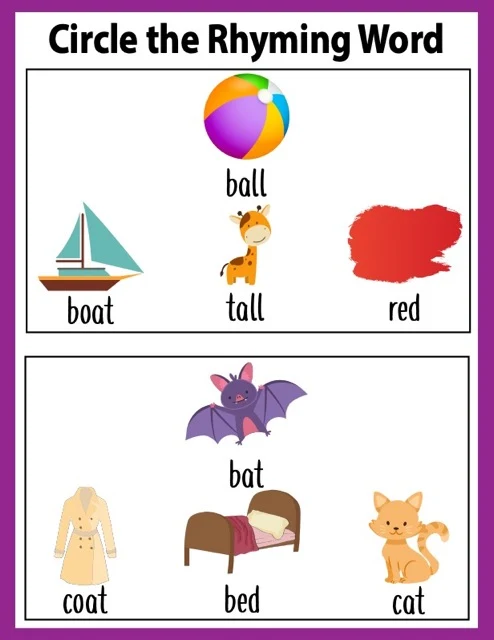
"Circle the Rhyming Word" Worksheets: These worksheets provide visual exercises for identifying rhyming pairs, as shown in "Testing Theme: Rhyming Words.pdf."
●
"Rhyming Word Cards": These versatile cards can be used for matching games, memory games, and sorting activities based on rhyming families.
Addressing Challenges with Rhyming
If a child struggles with rhyming, it is crucial to provide extra practice, break down the skill into simpler steps, and keep activities engaging. Consultation with the child's teacher for additional support and resources is also recommended.
Conclusion
Teaching rhyming words is an essential component of early literacy development. By incorporating engaging activities and employing a multi-sensory approach, parents and educators can effectively foster phonological awareness, vocabulary growth, and a lifelong love of language.
Rhyming Words: A Guide for Parents and Educators
Rhyming Words FAQ
What are rhyming words?
Rhyming words are words that have the same ending sound. For example, "cat" and "hat" rhyme because they both end with the "at" sound.
Why are rhyming words important?
Rhyming words are important for several reasons:
●
Phonological awareness: Recognizing rhymes helps children develop phonological awareness, which is the ability to hear and manipulate the sounds in words. This is a crucial skill for reading and spelling.
●
Vocabulary: Exposure to rhyming words can help children expand their vocabulary by introducing them to new words that share similar sounds.
●
Memory: Rhymes create patterns that make it easier for children to remember information.
●
Enjoyment of language: Rhymes make language fun and engaging, fostering a love of reading and poetry.
How can I help my child learn about rhyming words?
There are many fun and engaging ways to help your child learn about rhyming words:
●
Read rhyming books together: Nursery rhymes and Dr. Seuss books are great for introducing young children to the concept of rhyming.
●
Play rhyming games: Activities like "I Spy" with rhyming words, or creating silly rhymes together can make learning fun.
●
Sing rhyming songs: Singing songs with rhymes is a natural way to help children develop phonological awareness.
●
Use rhyming flashcards: Flashcards with pictures and words can help children visually connect rhyming pairs.
●
Encourage your child to create their own rhymes: Even simple rhymes can boost a child's confidence and creativity.
What are some examples of rhyming word families?
Some common rhyming word families include:
●
-at: cat, hat, bat, mat
●
-en: hen, pen, ten, men
●
-og: dog, log, fog, jog
●
-ing: sing, ring, wing, king
How can I use the "Circle the Rhyming Word" worksheets?
The "Circle the Rhyming Word" worksheets provide a visual way for children to practice identifying rhyming words.
●
Read the words aloud: Help your child read each set of words on the worksheet.
●
Identify the rhyming pair: Ask your child to find the two words that rhyme.
●
Circle the rhyming word: Have your child circle the word that rhymes with the first word in each set.
What are some other activities I can do with the "Rhyming Word Cards"?
The "Rhyming Word Cards" can be used for various interactive games and activities:
●
Matching game: Lay out the cards face down and have your child try to find matching rhyming pairs.
●
Memory game: Use the cards to play a memory game, focusing on remembering the location of rhyming words.
●
Sorting game: Have your child sort the cards into groups based on their rhyming families.
How can I tell if my child is struggling with rhyming?
If your child has difficulty recognizing rhyming words, they might:
●
Struggle to identify words that sound alike.
●
Have difficulty completing rhyming activities.
●
Show limited interest in rhyming books or songs.
What should I do if my child is struggling with rhyming?
If you notice your child struggling with rhyming, there are steps you can take:
●
Provide extra practice: Spend more time playing rhyming games and reading rhyming books.
●
Break down the skill: Start with simpler rhyming pairs and gradually introduce more challenging words.
●
Make it fun: Keep activities light and engaging to maintain your child's interest.
●
Consult with their teacher: Discuss your concerns with your child's teacher, who may be able to provide additional support or recommend resources.
Rhyming Words: A Comprehensive Study Guide
Rhyming Words Study Guide
Glossary of Key Terms
●
Rhyming Words: Words that share the same ending sound.
●
Phonological Awareness: The ability to hear and manipulate the sounds in words, a key skill for reading and spelling.
●
Rhyme Family: A group of words that share the same ending sound (e.g., -at: cat, hat, bat, mat).
●
Vocabulary: The collection of words a person understands and uses.
Short-Answer Quiz
Instructions: Answer each question in 2-3 sentences.
1.
Define rhyming words and explain their importance in language development.
2.
Describe two fun activities that parents or educators can use to teach children about rhyming words.
3.
Provide three examples of rhyming word families and list three words for each family.
4.
How can "Circle the Rhyming Word" worksheets benefit a child's understanding of rhymes?
5.
Explain how using rhyming flashcards can support a child's learning process.
6.
List three ways to use "Rhyming Word Cards" for interactive games.
7.
Identify three signs that a child might be struggling with rhyming.
8.
What steps can parents or educators take if a child is having difficulty with rhyming?
9.
Explain the relationship between rhyming and memory in early childhood.
10.
How does exposure to rhyming words contribute to a child's vocabulary growth?
Short-Answer Quiz Answer Key
1.
Rhyming words are words that share the same ending sound. They are important for language development because they build phonological awareness, expand vocabulary, enhance memory, and make language enjoyable.
2.
Two fun activities for teaching rhyming words are reading rhyming books together and playing rhyming games. Reading exposes children to the concept of rhyming in a fun and engaging way. Rhyming games, like "I Spy" with rhyming words, encourage active participation and reinforce learning through play.
3.
Three examples of rhyming word families are:
○
-at: cat, hat, bat
○
-op: hop, pop, top
○
-ug: hug, rug, bug
4.
"Circle the Rhyming Word" worksheets provide a visual and interactive way for children to practice identifying rhyming pairs. By circling the matching word, children actively demonstrate their understanding of the concept. The visual format also helps to reinforce the connection between the written word and its sound.
5.
Rhyming flashcards, with pictures and words, help children visually connect rhyming pairs. The combination of visual and auditory input strengthens the association between the sound and the written form of the word. They also provide a hands-on and engaging tool for practicing rhyming.
6.
"Rhyming Word Cards" can be used for matching games, memory games, and sorting activities. In a matching game, children find pairs of cards with rhyming words. Memory games challenge children to recall the locations of matching cards. Sorting activities encourage children to group cards based on their rhyming families.
7.
Signs a child may be struggling with rhyming include difficulty identifying words that sound alike, struggling to complete rhyming activities, and showing limited interest in rhyming books or songs. These behaviors may indicate a need for additional support and practice with rhyming skills.
8.
If a child struggles with rhyming, parents or educators can provide extra practice through games and books, break down the skill into simpler steps, make activities fun and engaging, and consult with the child's teacher for further support and resources. These strategies can help address the child's specific needs and foster their rhyming abilities.
9.
Rhyme and memory are interconnected because rhymes create patterns that make information easier to remember. The repetition of sounds in rhyming words provides a structure that aids in recall, particularly for young children who are developing their memory skills.
10.
Exposure to rhyming words introduces children to new words that share similar sounds, thus expanding their vocabulary. Hearing and recognizing rhyming patterns helps children make connections between words and their meanings, enriching their understanding of language.
Essay Questions
1.
Discuss the role of phonological awareness in early literacy development and explain how rhyming activities contribute to this skill.
2.
Analyze the benefits of using a multi-sensory approach (visual, auditory, kinesthetic) when teaching children about rhyming words.
3.
Evaluate the effectiveness of different strategies for teaching rhyming, such as reading rhyming books, playing rhyming games, and using flashcards.
4.
Explain how understanding rhyme can support a child's future success in reading and spelling.
5.
Design a lesson plan for a specific age group (e.g., preschool, kindergarten) that focuses on teaching rhyming words, incorporating various engaging activities.